Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Miyato, Naoaki; Kishimoto, Yasuaki; Li, J.*
Journal of Plasma Physics, 72(6), p.821 - 824, 2006/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Zonal flow behaviour and its effect on turbulent transport in reversed shear tokamaks are investigated by global nonlinear simulation of ion temperature gradient driven turbulence. When safety factor  is reduced, zonal flows in a minimum
is reduced, zonal flows in a minimum  region change from oscillatory ones to stationary ones and suppress the turbulent transport effectively. This result indicates that the change of zonal flow behaviour in the minimum
region change from oscillatory ones to stationary ones and suppress the turbulent transport effectively. This result indicates that the change of zonal flow behaviour in the minimum  region may trigger the formation of ion transport barriers.
region may trigger the formation of ion transport barriers.
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Takizuka, Tomonori; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Fujita, Takaaki; Kamada, Yutaka; Ide, Shunsuke; Koide, Yoshihiko
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 48(5A), p.A55 - A61, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:24.63(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Idomura, Yasuhiro; Tokuda, Shinji; Kishimoto, Yasuaki
Nuclear Fusion, 45(12), p.1571 - 1581, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:74.86(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Using a global gyrokinetic toroidal particle code, the toroidal electron temperature gradient driven (ETG) turbulence is studied in positive and reversed shear tokamaks. In the nolinear turbulent state, the ETG turbulence in the positive and reversed shear configurations show quite different structure formations. In the positive shear configuration, the ETG turbulence is dominated by streamers which have a ballooning type structure, and the electron temperature 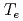 profile is quickly relaxed to the marginally stable state in a turbulent time scale. In the reversed shear configuration, quasi-steady zonal flows are produced in the regative shear region, while the positive shear region is characterized by streamers. Accordingly, the electron thermal diffusivity
profile is quickly relaxed to the marginally stable state in a turbulent time scale. In the reversed shear configuration, quasi-steady zonal flows are produced in the regative shear region, while the positive shear region is characterized by streamers. Accordingly, the electron thermal diffusivity 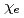 has a gap structure across the
has a gap structure across the 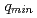 surface, and the
surface, and the 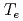 gradinet is sustained above the marginal value for a long time in the quasi-steady phase. The results suggest a stiffness of the
gradinet is sustained above the marginal value for a long time in the quasi-steady phase. The results suggest a stiffness of the 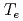 profile in positive shear tokamaks, and a possibility of the Te transport barrier in reversed shear tokamaks.
profile in positive shear tokamaks, and a possibility of the Te transport barrier in reversed shear tokamaks.
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Takizuka, Tomonori; Ozeki, Takahisa
Nuclear Fusion, 45(8), p.933 - 941, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:41.32(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)We have investigated profile formation and sustainment of current hole (CH) plasma by 1.5D transport simulations with current limit model inside CH based on Axisymmetric Tri-Magnetic-Islands equilibrium. Sharp reduction of anomalous transport in RS region can reproduce JT-60U experiments. The transport becomes neoclassical-level in RS region, which results in autonomous profile formation of ITB and CH through large bootstrap current. ITB width determined by neoclassical-level transport agrees with that in JT-60U. Energy confinement inside ITB agrees with JT-60U scaling. The scaling means that core plasma inside ITB is governed by MHD equilibrium limit, i.e., autonomous limitation of energy confinement. The plasma with large CH is sustained with full current drive by bootstrap current. The plasma with small CH and small bootstrap current fraction shrinks due to penetration of inductive current. This shrink is prevented and CH size can be controlled by appropriate external CD. CH plasma is found to respond autonomically to external CD. Application of CH plasma to reactor is discussed.
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Takizuka, Tomonori; Ozeki, Takahisa
Proceedings of 20th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2004) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2004/11
Profile formation and sustainment of tokamak plasmas with current hole (CH) have been investigated by using 1.5D transport simulations. A current limit model inside CH based on the Axisymmetric Tri-Magnetic-Islands equilibrium is introduced. We found that the sharp reduction of anomalous transport in the reversed-shear (RS) region can reproduce JT-60U experiment. The transport becomes neoclassical-level in RS region, which results in the autonomous formation of internal transport barrier (ITB) and CH through large bootstrap current. ITB width determined by neoclassical-level transport agrees with that in JT-60U. Energy confinement inside ITB agrees with JT-60U scaling, which means autonomous limitation of energy confinement. The plasma with large CH is sustained with the full current drive by bootstrap current. The plasma with small CH and small bootstrap current fraction shrinks due to inductive current penetration. This shrink is prevented and the CH size can be controlled by appropriate external current drive (CD). The CH plasma is found to respond autonomically to external CD.
 n eigenmodes
n eigenmodesKonovalov, S. V.; Mikhailovskii, A. B.*; Shirokov, M. S.*; Kovalishen, E. A.*; Ozeki, Takahisa
Physics of Plasmas, 11(9), p.4531 - 4534, 2004/09
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:53.19(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Konovalov, S. V.; Mikhailovskii, A.*; Kovalishen, E.*; Ozeki, Takahisa; Takizuka, Tomonori; Shirokov, M. S.*
Proceedings of 20th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2004) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2004/00
Alfven eigenmodes in tokamaks with reversed magnetic shear are studied theoretically by incorporating into the mode description the effects known theories of Global, Kinetic and Toroidal Alfven Eigenmodes. In particular mode forming effect due to thermal plasma density gradient is examined. Criteria of the fast ion density and its gradient on the existence of a localized solution of the eigenmode equation is softened by this effect. Effects of finite Larmor radius, continuum damping and fast ion density gradient are also studied.
Fujita, Takaaki; JT-60 Team
Nuclear Fusion, 43(12), p.1527 - 1539, 2003/12
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:68.04(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Recent JT-60U results toward high integrated performance are reported with emphasis on the projection to the reactor-relevant regime. N-NB and EC power increased up to 6.2 MW and 3 MW, respectively. A high betap H-mode plasma with full non-inductive current drive has been obtained at 1.8 MA and the fusion triple product reached 3.1E20m keVs. NTM suppression with EC was accomplished using a real-time feedback control system and improvement in betaN was obtained. A stable existence of current hole was observed. High DT-equivalent fusion gain of 0.8 was maintained for 0.55 s in a plasma with a current hole. The current profile control in high bootstrap current reversed shear plasmas was demonstrated using N-NB and LH. A new operation scenario has been established in which a plasma with high bootstrap current fraction and ITBs is produced without the use of OH coil. A new type of AE mode has been proposed and found to explain the observed frequency chirp quite well. Ar exhaust with EC heating was obtained in a high betap mode plasma.
keVs. NTM suppression with EC was accomplished using a real-time feedback control system and improvement in betaN was obtained. A stable existence of current hole was observed. High DT-equivalent fusion gain of 0.8 was maintained for 0.55 s in a plasma with a current hole. The current profile control in high bootstrap current reversed shear plasmas was demonstrated using N-NB and LH. A new operation scenario has been established in which a plasma with high bootstrap current fraction and ITBs is produced without the use of OH coil. A new type of AE mode has been proposed and found to explain the observed frequency chirp quite well. Ar exhaust with EC heating was obtained in a high betap mode plasma.
Takizuka, Tomonori
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 79(11), p.1123 - 1129, 2003/11
no abstracts in English
Miura, Yukitoshi; JT-60 Team
Physics of Plasmas, 10(5), p.1809 - 1815, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:31.59(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Kubo, Hirotaka; Sakurai, Shinji; Higashijima, Satoru; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Itami, Kiyoshi; Konoshima, Shigeru; Nakano, Tomohide; Koide, Yoshihiko; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 313-316(1-3), p.1197 - 1201, 2003/03
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:75.71(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Takizuka, Tomonori
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 78(12), p.1282 - 1284, 2002/12
An idea of a new equilibrium of a strongly-reversed-shear tokamak plasma with a current hole is proposed. This equilibrium configuration called "Axisymmetric Tri-Magnetic-Islands (ATMI) equilibrium" has three islands, a central-negative-current island and side-positive-current islands, along the R direction and two x-points along the Z direction. The equilibrium is stable with the elongation coils when the current in the ATMI region is limited small.
JT-60 Team
JAERI-Review 2002-022, 149 Pages, 2002/11
no abstracts in English
Tobita, Kenji; Kusama, Yoshinori; Shinohara, Koji; Nishitani, Takeo; Kimura, Haruyuki; Kramer, G. J.*; Nemoto, Masahiro*; Kondoh, Takashi; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Morioka, Atsuhiko; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology (JT-60 Special Issue), 42(2-3), p.315 - 326, 2002/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:47.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)Energetic particle experiments in JT-60U are summarized, mainly covering ripple loss and Alfven eigenmodes (AE modes). Significant loss was observed for 85 keV NBI ions and fusion-produced tritons increased when toroidal field ripple at the plasma surface, especially in reversed shear plasma. Measurement of hot spots on the first wall due to ripple loss confirmed agreement with code predictions, validating the modeling incorporated in an orbit-following Monte Carlo code. A variety of AE modes were destabilized in ICRF minority heating and negative-ion-based NBI (N-NBI) heating. Most of the observed modes are gap modes identified to be TAE, EAE and NAE. Interesting finding is pulsating modes accompanying frequency sweep, which were destabilized by N-NBI and sometimes induced a beam ion loss of up to 25%. Also presented are energetic particle issues in auxiliary heating with ICRF and N-NBI.
Ushigusa, Kenkichi; Ide, Shunsuke; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Suzuki, Takahiro; Kamada, Yutaka; Fujita, Takaaki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Naito, Osamu; Matsuoka, Mamoru*; Kondoh, Takashi; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology (JT-60 Special Issue), 42(2-3), p.255 - 277, 2002/09
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:15.15(Nuclear Science & Technology)Studies on non-inductive current drive and development of an integrated steady-state high performance operation in JT-60 are reviewed. Experiments on lower hybrid current drive in JT-60 haven shown a large non-inductive current up to 3.5MA, high current drive efficiency of 3.6x1019m-2A/W. Basic studies on LH waves in JT-60 have contributed to understand current drive physics. Significant progress in neutral beam current drive has been made in JT-60 by testing the performance of negative ion based NBI (N-NBI). The CD efficiency of ~1.5x1019m-2A /W, and N-NB driven current of ~1MA have been demonstrated in N-NBCD. Strongly localized driven current by electron cyclotron current drive was identified with a fundamental O-mode scheme. Efficiency of 0.5x1019m-2A/W and EC driven current of 0.2MA were achieved and suppression of neo-classical tearing mode was demonstrated. Based on these developments, two integrated steady-state operation scenarios were developed in JT-60, which are reversed magnetic shear (R/S) plasmas and high bp ELMy H-mode. In these operation regimes, discharges have been sustained near the steady-state current profile under full non-inductive current drive. High performance plasmas with a high nDotETio and at high normalized density were also produced under fully non-inductive condition in high bp ELMy H-mode and R/S mode.
; Ishii, Yasutomo; ; Tokuda, Shinji; Ozeki, Takahisa; S.Hudson*; Kishimoto, Yasuaki
Chinese Physics Letters, 362, p.83 - 84, 1999/09
no abstracts in English

 discharges in JT-60U
discharges in JT-60UKoide, Yoshihiko; Mori, Masahiro; Fujita, Takaaki; Shirai, Hiroshi; Hatae, Takaki; Takizuka, Tomonori; Kimura, Haruyuki; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Isei, Nobuaki; Isayama, Akihiko; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 40(5), p.641 - 645, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:61.77(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Ishida, Shinichi
Physical Review Letters, 79(20), p.3917 - 3921, 1997/11
Times Cited Count:86 Percentile:92.31(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Neyatani, Yuzuru; JT-60 Team
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 38(12A), p.181 - 191, 1996/00
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:46.08(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English